Sql Server Error 1474 State 1
Mar 06, 2013 This blog is a diary, which helps me as well as others while surfing about SQL Server. Some articles are written by me some were taken as reference from others websites. – You need to run the SQL service with the same service account on each server (of course you can change that but that is recommended I read somewhere). So I looked at all the three servers and checked the SQL service account used there.
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQL Server RAISERROR statement to generate user-defined error messages.
If you develop a new application, you should use the THROW statement instead.
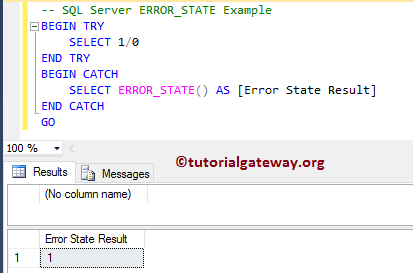
Syntax error converting the varchar value to a column of data type int. Error Message: Server: Msg 245, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 Syntax error converting the. SQL Server RAISERROR examples. Let’s take some examples of using the RAISERROR statement to get a better understanding. A) Using SQL Server RAISERROR with TRY CATCH block example. In this example, we use the RAISERROR inside a TRY block to cause execution to jump to the associated CATCH block.
SQL Server RAISEERROR statement overview
The RAISERROR statement allows you to generate your own error messages and return these messages back to the application using the same format as a system error or warning message generated by SQL Server Database Engine. In addition, the RAISERROR statement allows you to set a specific message id, level of severity, and state for the error messages.
The following illustrates the syntax of the RAISERROR statement:
Let’s examine the syntax of the RAISERROR for better understanding.
message_id
The message_id is a user-defined error message number stored in the sys.messages catalog view.
Sql Server Error 1474 State 10th
To add a new user-defined error message number, you use the stored proceduresp_addmessage. A user-defined error message number should be greater than 50,000. By default, the RAISERROR statement uses the message_id 50,000 for raising an error.
Hdd low level format tool 4.25. HDDGURU HDD Low Level Format Tool is an application to low-level format in order to process a true and complete disk formatting. Some viruses cannot be removed by antivirus. Moreover, standard formatting cannot delete these malicious applications. The unique solution resides on using a low-level format and HDD Low Level Format Tool is a good choice. HDD Low Level Format Tool is a utility for low-level hard disk drive formatting. Supported interfaces: S-ATA (SATA), IDE (E-IDE), SCSI, SAS, USB, FIREWIRE. Big drives (LBA-48) are supported. Supported Manufacturers: Maxtor, Hitachi, Seagate, Samsung, Toshiba, Fujitsu, IBM, Quantum, Western Digital, and almost any other not listed here. Feb 03, 2019 HDD Low Level Format Tool is a freeware utility for low-level hard disk drive formatting. This small program will erase, Low-Level Format and re-certify a SATA, IDE or SCSI hard disk drive.
The following statement adds a custom error message to the sys.messages view:
To verify the insert, you use the following query:
To use this message_id, you execute the RAISEERROR statement as follows:
Here is the output:
To remove a message from the sys.messages, you use the stored procedure sp_dropmessage. For example, the following statement deletes the message id 50005:
message_text
The message_text is a user-defined message with formatting like the printf function in C standard library. The message_text can be up to 2,047 characters, 3 last characters are reserved for ellipsis (…). If the message_text contains 2048 or more, it will be truncated and is padded with an ellipsis.
When you specify the message_text, the RAISERROR statement uses message_id 50000 to raise the error message.
The following example uses the RAISERROR statement to raise an error with a message text:
The output will look like this:
severity
The severity level is an integer between 0 and 25, with each level representing the seriousness of the error.
state
The state is an integer from 0 through 255. If you raise the same user-defined error at multiple locations, you can use a unique state number for each location to make it easier to find which section of the code is causing the errors. For most implementations, you can use 1.
WITH option
The option can be LOG, NOWAIT, or SETERROR:
WITH LOGlogs the error in the error log and application log for the instance of the SQL Server Database Engine.WITH NOWAITsends the error message to the client immediately.WITH SETERRORsets theERROR_NUMBERand@@ERRORvalues to message_id or 50000, regardless of the severity level.
SQL Server RAISERROR examples
Let’s take some examples of using the RAISERROR statement to get a better understanding.
A) Using SQL Server RAISERROR with TRY CATCH block example
In this example, we use the RAISERROR inside a TRY block to cause execution to jump to the associated CATCH block. Inside the CATCH block, we use the RAISERROR to return the error information that invoked the CATCH block.
Here is the output:
B) Using SQL Server RAISERROR statement with a dynamic message text example
Sql Server Error 1474 State 1007
The following example shows how to use a local variable to provide the message text for a RAISERROR statement:
The output is as follows:
When to use RAISERROR statement
You use the RAISERROR statement in the following scenarios:
- Troubleshoot Transact-SQL code.
- Return messages that contain variable text.
- Examine the values of data.
- Cause the execution to jump from a
TRYblock to the associatedCATCHblock. - Return error information from the
CATCHblock to the callers, either calling batch or application.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQL Server RAISERROR statement to generate user-defined error messages.
Today my colleague had issue that SQL server instance is not starting on.
It is a SQL 2016 and had seven instances with 24 GB of total OS RAM. Same again, one of the SQL instance memory configured incorrectly. It is a alwaysON secondary replica.
We know where we have to look, when we cannot start SQL service.
Run — Eventvwr — Windows logs –Application and system.
One more: Open SQL server errorlog file in notepad and review as well.
You can get the error log location in the configuration manger — startup parameters.
2019-01-30 04:43:14.73 spid6s Error: 701, Severity: 17, State: 123.
2019-01-30 04:43:14.73 spid6s There is insufficient system memory in resource pool ‘internal’ to run this query.
2019-01-30 04:43:14.73 Server Error: 17300, Severity: 16, State: 1. (Params:). The error is printed in terse mode because there was error during formatting. Tracing, ETW, notifications etc are skipped.
2019-01-30 04:43:14.73 Server Error: 17300, Severity: 16, State: 1. (Params:). The error is printed in terse mode because there was error during formatting. Tracing, ETW, notifications etc are skipped.
2019-01-30 04:43:14.74 Server Error: 17300, Severity: 16, State: 1. (Params:). The error is printed in terse mode because there was error during formatting. Tracing, ETW, notifications etc are skipped.
2019-01-30 04:43:14.74 Server Error: 17300, Severity: 16, State: 1. (Params:). The error is printed in terse mode because there was error during formatting. Tracing, ETW, notifications etc are skipped.
2019-01-30 04:43:14.74 Server Error: 17300, Severity: 16, State: 1. (Params:). The error is printed in terse mode because there was error during formatting. Tracing, ETW, notifications etc are skipped.
2019-01-30 04:43:14.74 Server Error: 17300, Severity: 16, State: 1. (Params:). The error is printed in terse mode because there was error during formatting. Tracing, ETW, notifications etc are skipped.
2019-01-30 04:43:14.74 spid6s SQL Server shutdown has been initiated
2019-01-30 04:43:14.74 spid6s Error: 19032, Severity: 10, State: 1. (Params:). The error is printed in terse mode because there was error during formatting. Tracing, ETW, notifications etc are skipped.
To fix:
We need to start SQL service in minimal configuration -f or single user mode -m and have to change the memory setting by GUI or T-SQL.
By GUI you have connect normal and go to property and change max and min memory and remove that startup flag and recycle the SQL service.
By T-SQL cancel the connection and click new query window and use following T-SQL
sp_configure ‘show advan’,1;reconfigure
Go
Sp_configure ‘max server memory (MB)’,’1024′;reconfigure